The use of electronic signatures has dramatically increased in recent years, attributed in part by new technologies and the pandemic, which rapidly accelerated the need for remote solutions. In a digital world where identity theft considerably impacts remote transactions, the need for secure electronic signatures as part of a robust and rigorous Know Your Customer (KYC) process has never been more important.
Electronic signatures are used in various sectors such as real estate, banking, insurance, or public services.
Are electronic signatures legally valid?
According to Article 1367 of the French Civil Code, electronic signatures have the same legal value as a handwritten signature. It is therefore admissible as evidence in court if it meets the conditions of the European Regulation, Electronic Identification and Trust Service (EIDAS) regulation, which aims to increase trust in digital transactions.
According to EIDAS, there are three different security levels of electronic signatures (eSignatures).
eSignature security levels.
Simple signature
Simple signatures are used for a small (or low risk) transaction since it does not require identity verification. Documents that require this level of signature include invoices, membership contracts or quotations. However, in some cases, these documents could also be reinforced by an authentication step, such as a OTP (One Time Password), which is sent by SMS to the signatory to verify his/her identity.
Advanced signature
For higher levels of security, eIDAS requires identity verification. “Advanced” signatures integrate a KYC step into the process, allowing the user to verify that they are who they say they are. An advanced electronic signature is a digital signature based on an advanced certificate uniquely identifying the signer. The signature keys are used with a high level of confidence by the signatory (who has sole control of the signing key)
Qualified signature
The qualified electronic signature (QES) has the highest security level of all e-signatures. In addition to the requirements for an advanced electronic signature, a QES is created by a qualified signature creation device, and it is based on a qualified certificate for electronic signatures. These higher levels of security apply to certain financial transactions or any documents with significant legal standing, such as life insurance, real estate sales agreements or bank account opening contracts.
KYC for electronic signatures.
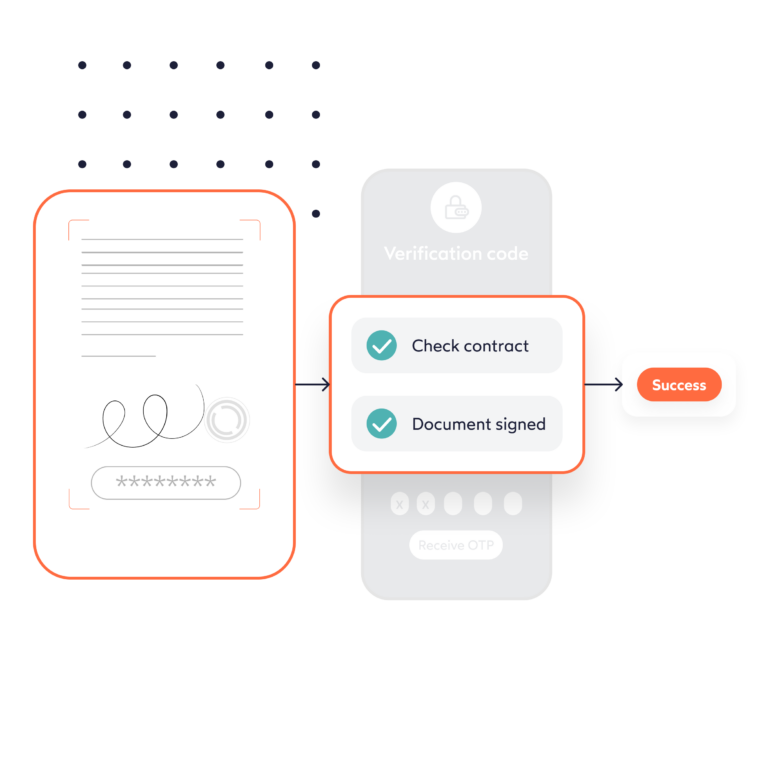
The KYC process is essential for electronic signatures to meet eIDAS requirements. The overall goal of KYC – to define and verify the identity of the customer – can occur at different stages in the customer journey: either when entering into a relationship or when electronically signing the contract. In the case of a signature, the authenticity and integrity of the signed document are guaranteed for both parties, and the identity of the signatory is secured. The identity verification step for electronic signatures can be achieved in two ways: face to face or remotely. NOTE: in the event of a legal dispute over an advanced signature, for example, the party requesting the signature must prove its authenticity. In the case of a qualified signature, the signatory person must prove his identity was defrauded.
As mentioned before, eIDAS provides a framework for electronic signatures by imposing different levels of security depending on the nature of the transactions.
Fight identity theft with KYC.
In financial services, in order to open an online bank account, the user must provide personal information by having their ID verified. Only when their identity has been validated can they open a bank account. In this regard, KYC can help in the fight against identity fraud and money laundering, and service to establish a level of trust within the service.
Integrating a KYC step into an electronic signature process ensures the integrity of the signatory, creates a trusting environment and reinforces security, depending on the required level of trust. As such, it is beneficial both to the company and the user.
In addition to increased trust and security, electronic signatures can also contribute to a superior customer experience, and even improve conversion rates.
Provide an optimal customer experience thanks to KYC.
Customer experience is a competitive differentiator. Onboarding, in particular is a pivotal stage of the journey. Approximately 40% of customers abandon onboarding if it takes too long or requires too much personal information.
Electronic signature functionality is seen as one of the easiest and most valuable services to overhaul as part of a company’s digital transformation efforts. Benefits are numerous, including cost savings, task automation, and user experience improvement.
The process needs to be as fluid, simple and fast as possible.
Electronic signatures and the pandemic
The pandemic accelerated the need for digitized processes. This was especially the case in the human resources sector, which had to adapt and quickly implement remote employment contract signatures for new hires. KYC also played a major role in verifying the identity of the people that companies hire.
Paperless. Seamless. Limitless.
By

Rayissa Armata
Senior Head of Regulatory Affairs at IDnow
Connect with Rayissa on LinkedIn